Decoding PNPLA3-Mediated Pathogenesis in MASLD
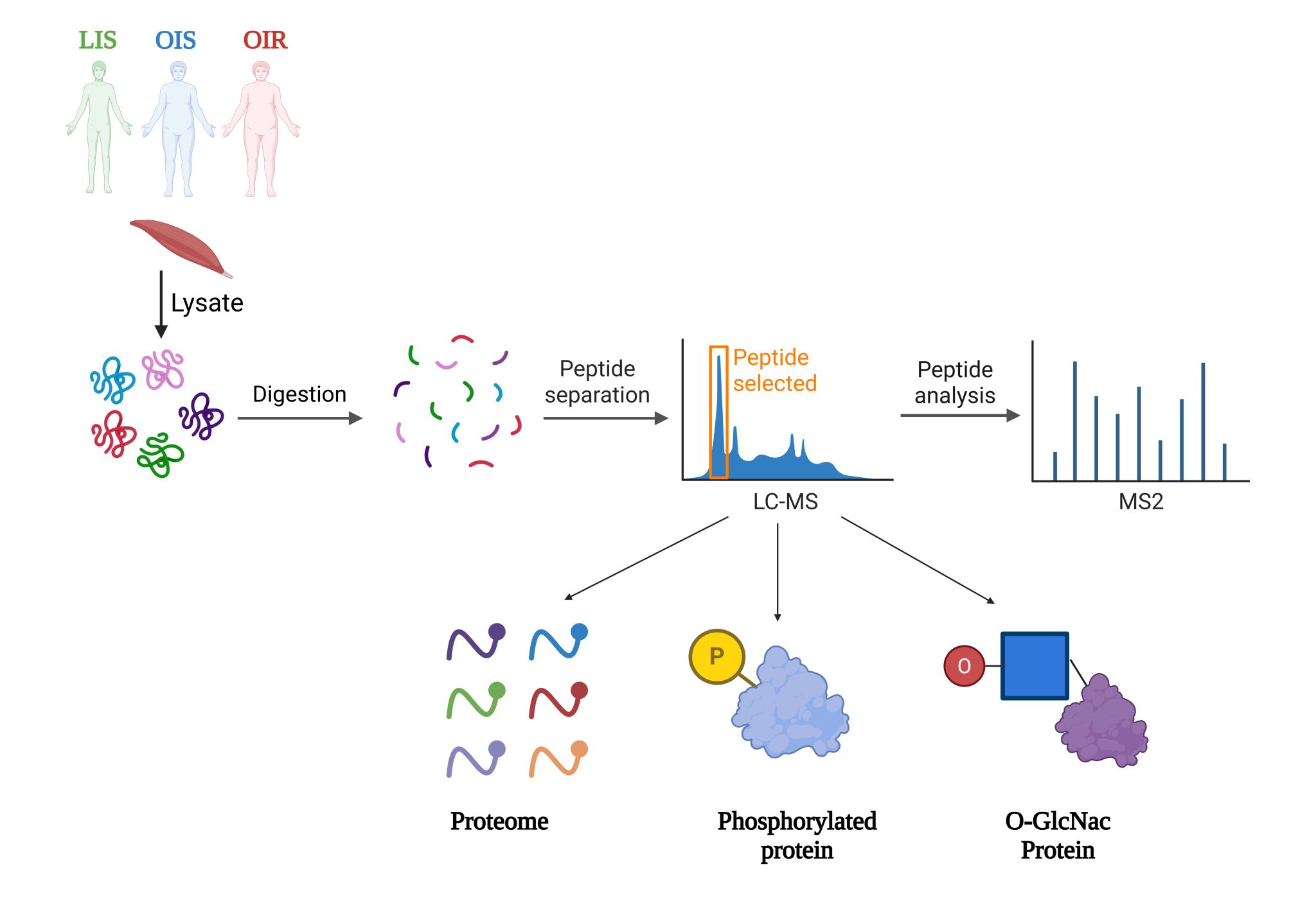
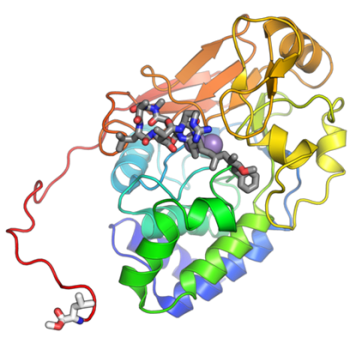
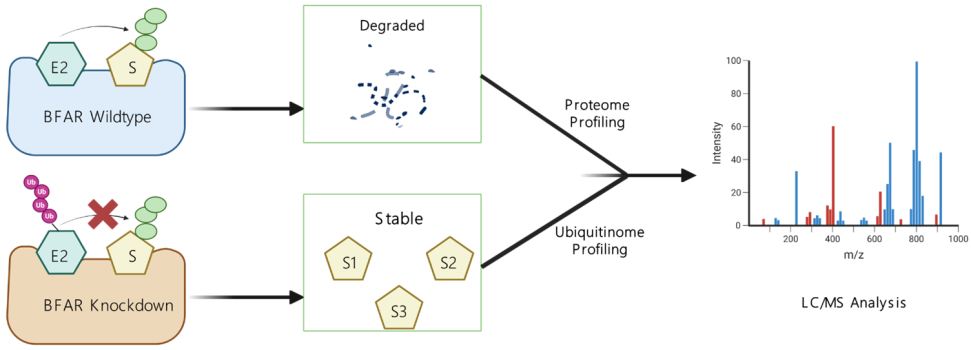
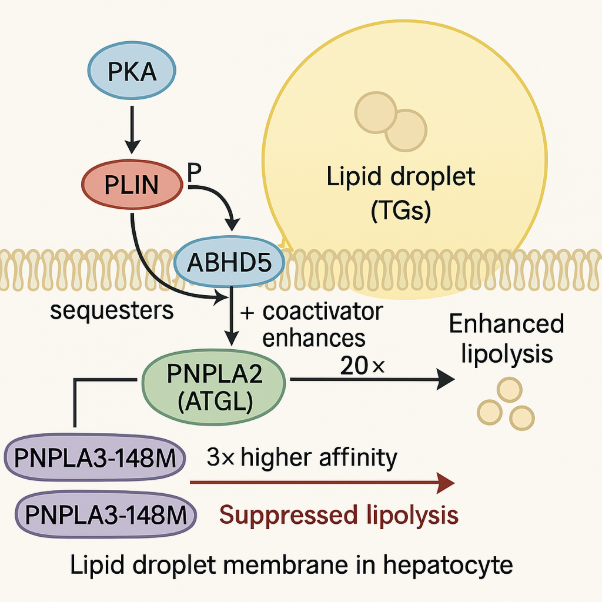
Our PNPLA3 project investigates the molecular mechanisms by which the I148M mutation in PNPLA3 contributes to the development of Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Using integrative approaches, including protein-protein docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, and LC-MS/MS-based proteomics & interactomics, we demonstrate that PNPLA3-I148M competitively sequesters the coactivator ABHD5 away from its primary lipase partner, PNPLA2 (ATGL). This impaired lipolytic signaling leads to hepatic triglyceride accumulation—a key hallmark of MAFLD. Ongoing efforts are focused on identifying potential small-molecule modulators of PNPLA3-ABHD5 interactions to restore lipolysis and provide novel therapeutic strategies for fatty liver disease.